How To Create Database In Arduino
Arduino - MySQL
Arduino can collect sensor data and store it on the MySQL database. Arduino can also get data (command) from MySQL database and control LED, motor, actuator, device...
In this tutorial, we are going to learn:
-
The best way for Arduino to interact with MySQL database
-
How Arduino insert data to MySQL database
-
How Arduino update data to MySQL database
-
How Arduino get data from MySQL database
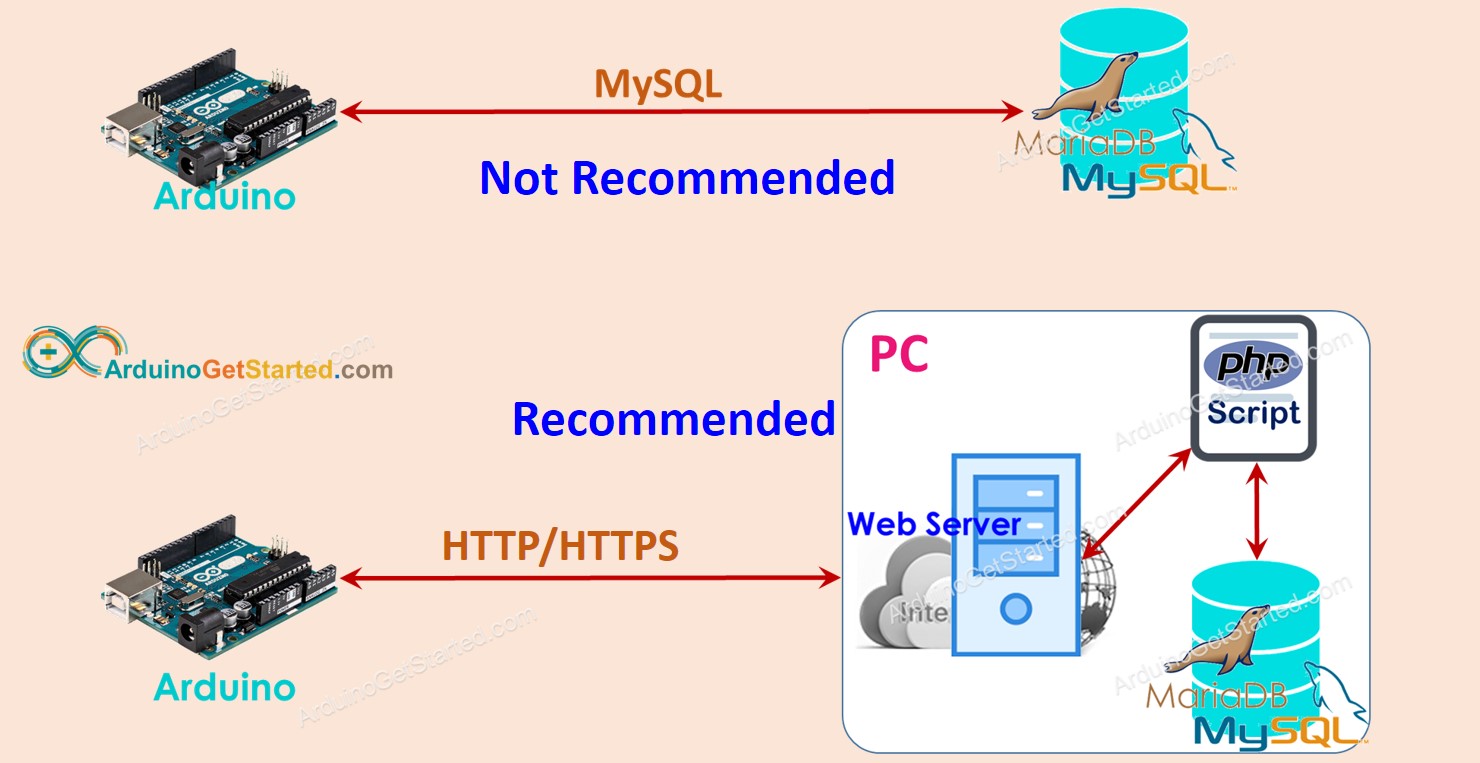
If you do not have much knowledge of the system architecture, two terms: MySQL Database and MySQL Server can be understood as the same. You will find the differences later when you know a lot about the system architecture.
There are two ways for Arduino to interact with the MySQL database:
-
Arduino interacts directly to MySQL Server via MySQL connection (called direct way)
-
Arduino interacts indirectly to MySQL Server via HTTP connection (called indirect way)
Let's find the best one.

This sounds simpler but there are many disadvantages:
-
This allows a MySQL User account to remotely access MySQL database ⇒ This is dangerous from the security point of view, even if limited privileges were granted to the user account.
-
The data MUST be processed in Arduino and/or MySQL server ⇒ This increases the complexity of Arduino code and MySQL script. Especially, it consumes a lot of Arduino resources (Memory and CPU usage).
-
MySQL server may return a very big amount of data to Arduino in some cases ⇒ This can make Arduino run out of memory.
-
Most of the available MySQL libraries do not support SSL/TLS. The data including username/password will be sent in plain text ⇒ another security issue.
This indirect way solves all problems that the direct way has. Before seeing how the indirect way overcomes the disadvantages of the direct way, let's see how it works first
-
Step 1: Arduino makes HTTP Request to Web Server
-
Step 2: Web Server runs PHP script
-
Step 3: PHP script gets data from HTTP Request, processes the data, and then interacts with MySQL database.
-
Step 4: PHP script processes the result and returns the result to Arduino via HTTP Response
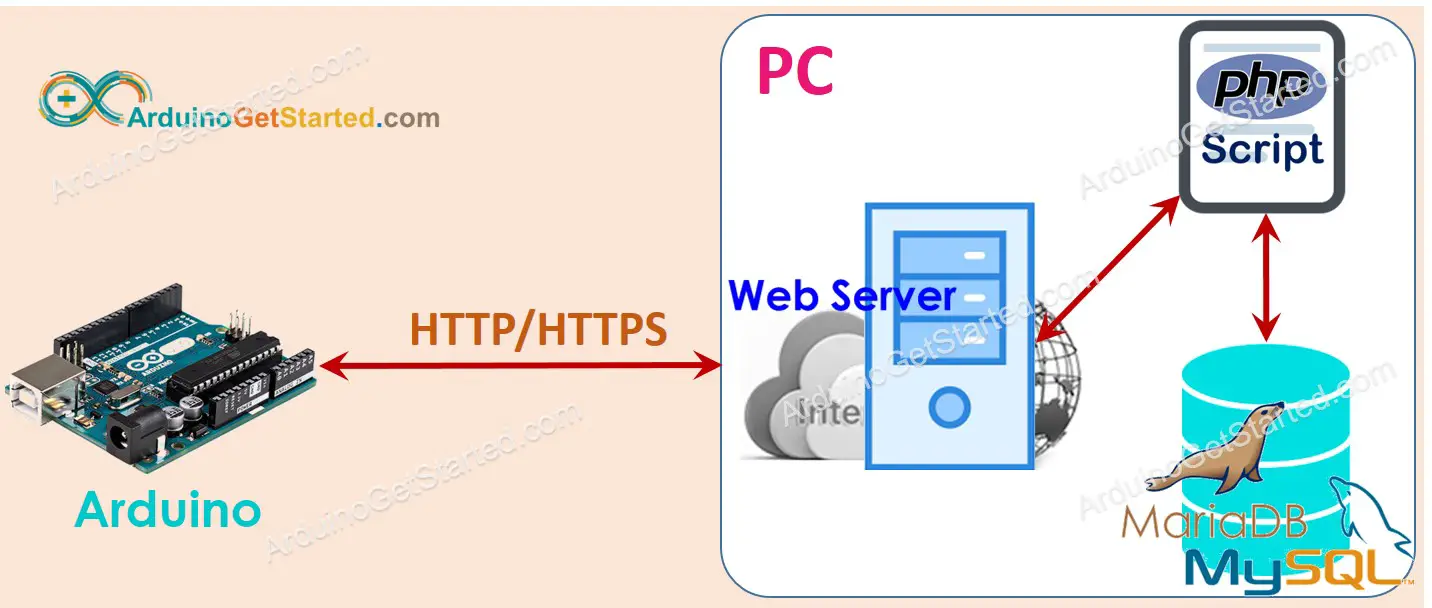
In this tutorial, the Web server, MySQL server will be installed on PC.
It looks complicated but not. Now Let's see how the indirect way overcomes the disadvantages of the direct way.
-
By installing the MySQL server and HTTP server in the same physical server, We can limit a MySQL User account to access localhost ONLY. Moreover, the username/password of the MySQL account is stored on Server (step 3), this makes the system more secure.
-
Data is processed by a PHP script(step 3 and step 4). This reduces the works and complexity for Arduino and MySQL servers. Processing data using PHP code is much easier than the Arduino code and MySQL script.
-
PHP script can process the data and send only necessary data to Arduino (Step 4) to prevent Arduino from running out of memory.
-
Most of Ethernet/WiFi libraries supports TLS/SSL that allows us to make HTTPS request. By using HTTPS, the data is encrypted and securely exchanged over the Internet.
In step 1, we can use another username/password to do authentication between Arduino and Web Server. Please note that the HTTP username/password should be different from the MySQL username/password for security reasons.
With those advantages, the rest of this tutorial will present how to use Arduino with MySQL via indirect way.
We need to do the following step:
-
Install MySQL server, Web server, and PHP on your PC
-
Enable MySQL and Web server
-
Create a MySQL User account
-
Create a MySQL database
-
Create a MySQL table
-
Write one or more PHP script files
-
Write Arduino code
Now let's do it step-by-step.
Fortunately, the XAMPP package includes all of these. We just need to install one time
-
Install it.
After installing, you will see C:\xampp\htdocs folder on your PC. This is where you put PHP code (see later).
-
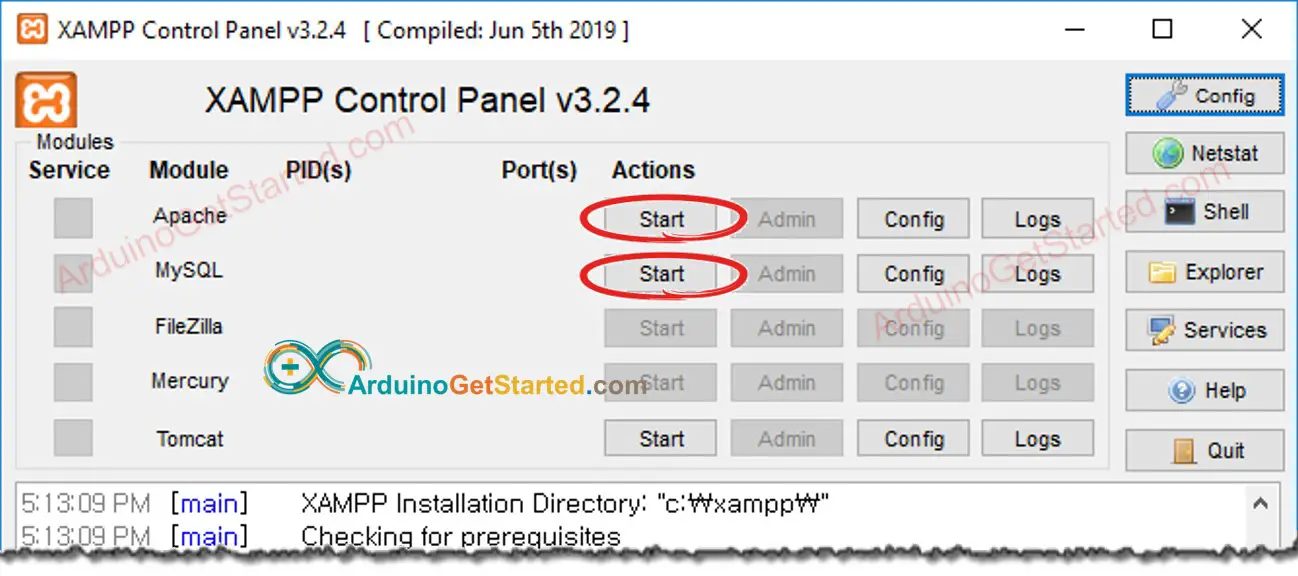
Open XAMPP Control Panel
-
Click Start button to enable MySQL and Web server (See the below image)
We will create a MySQL account that can connect to the MySQL database from localhost only.
-
Even if username/password are revealed, the attackers still cannot access your MySQL database unless they take control of your PC.
-
Because PHP and MySQL are installed on the same PC, PHP can use this username/password to connect to the MySQL database.
Let's create a MySQL user account with username is Arduino and password is ArduinoGetStarted.com:
-
Open Command Prompt on your PC. Do not close it until the end of the tutorial.
-
Type the following command on Command Prompt:
C:\Users\youruser>cd C:\xampp\mysql\bin C:\xampp\mysql\bin>
-
By default, MySQL has root account without password. You should add password
(e.g. your-root-password) for root account by typing the following command on Command Prompt:
mysqladmin -u root password your-root-password
C:\xampp\mysql\bin>mysqladmin -u root password your-root-password C:\xampp\mysql\bin>
-
Type the following command on Command Prompt:
-
Type your-root-password and press Enter
C:\xampp\mysql\bin>mysql.exe -u root -p Enter password: ****************** Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 9 Server version: 10.4.6-MariaDB mariadb.org binary distribution Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]>
-
Create a MySQL user account with username is Arduino and password is ArduinoGetStarted.com by coping the below commands and paste on Command Prompt:
CREATE USER 'Arduino'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ArduinoGetStarted.com'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'Arduino'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'Arduino'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ArduinoGetStarted.com'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.005 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'Arduino'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.005 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]>
Now you successfully created and MySQL user account. Memorize the username/password, It will be used in PHP script.
Let's create a database named db_arduino by typing the following command on Command Prompt:
CREATE DATABASE db_arduino CHARACTER SET = 'utf8' COLLATE = 'utf8_general_ci';
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE db_arduino CHARACTER SET = 'utf8' COLLATE = 'utf8_general_ci'; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.003 sec) MariaDB [(none)]>
Let's create a database named tbl_temp by coping the below commands and paste on Command Prompt:
USE db_arduino; CREATE TABLE tbl_temp ( temp_id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, temp_value FLOAT DEFAULT 0.00, PRIMARY KEY (temp_id) );
MariaDB [(none)]> USE db_arduino; Database changed MariaDB [db_arduino]> MariaDB [db_arduino]> CREATE TABLE tbl_temp ( -> temp_id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> temp_value FLOAT DEFAULT 0.00, -> PRIMARY KEY (temp_id) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.044 sec) MariaDB [db_arduino]>
Create a PHP file named insert_temp.php that gets temperature from HTTP Request and inserts it into the database.
<?php if(isset($_GET["temperature"])) { $temperature = $_GET["temperature"]; $servername = "localhost"; $username = "Arduino"; $password = "ArduinoGetStarted.com"; $dbname = "db_arduino"; $conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname); if ($conn->connect_error) { die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error); } $sql = "INSERT INTO tbl_temp (temp_value) VALUES ($temperature)"; if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) { echo "New record created successfully"; } else { echo "Error: " . $sql . " => " . $conn->error; } $conn->close(); } else { echo "temperature is not set"; } ?>
-
Place this file inside C:\xampp\htdocs folder
-
Get your PC's IP address. If you do not know how to, google it.
-
The output on the web browser
-
Check whether data is stored in database by typing the following command on Command Prompt:
MariaDB [db_arduino]> SELECT * from tbl_temp; +---------+------------+ | temp_id | temp_value | +---------+------------+ | 1 | 27.5 | +---------+------------+ 1 row in set (0.001 sec) MariaDB [db_arduino]>
As you can see, the temperature of 27.5 is stored in the database. The next step is to write Arduino that makes a similar HTTP Request to your PC.
We will use Arduino Uno and Ethernet Shield for the test
The below Arduino code makes HTTP to your PC to insert a temperature of 29.1°C into the database
#include <SPI.h> #include <Ethernet.h> byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED }; EthernetClient client; int HTTP_PORT = 80; String HTTP_METHOD = "GET"; char HOST_NAME[] = "192.168.0.26"; String PATH_NAME = "/insert_temp.php"; String queryString = "?temperature=29.1"; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); if (Ethernet.begin(mac) == 0) { Serial.println("Failed to obtaining an IP address using DHCP"); while(true); } if(client.connect(HOST_NAME, HTTP_PORT)) { Serial.println("Connected to server"); client.println(HTTP_METHOD + " " + PATH_NAME + queryString + " HTTP/1.1"); client.println("Host: " + String(HOST_NAME)); client.println("Connection: close"); client.println(); while(client.connected()) { if(client.available()){ char c = client.read(); Serial.print(c); } } client.stop(); Serial.println(); Serial.println("disconnected"); } else { Serial.println("connection failed"); } } void loop() { }
-
Stack Ethernet Shield on Arduino Uno
-
Connect Ethernet Cable to Ethernet Shield
-
Connect Arduino Uno to PC via USB cable
-
Change IP address on the code by your PC's IP address
-
Compile and upload code to Arduino
-
Open Serial Monitor
-
The result on Serial Monitor
-
Check whether data is stored in database by typing the following command on Command Prompt:
Connected to server HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 12 Jan 2021 07:52:22 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.39 (Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1c PHP/7.3.8 X-Powered-By: PHP/7.3.8 Content-Length: 31 Connection: close Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 New record created successfully disconnected
MariaDB [db_arduino]> SELECT * from tbl_temp; +---------+------------+ | temp_id | temp_value | +---------+------------+ | 1 | 27.5 | | 2 | 29.1 | +---------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [db_arduino]>
As you can see, the temperature 29.1 is stored in database.
In the above example, we have learned how to insert data into the MySQL database. For updating and getting data from the database, it is similar. You only need to change MySQL queries on the PHP script. You can learn more from W3Schools
To increase the security
-
You can change Arduino code to make HTTPS instead of HTTP. See Arduino - HTTPS
-
You can use a username/password to do authentication between Arduino and the Web server. See Basic access authentication
※ NOTE THAT:
To make a complete system with the highest security level, we need to do more (such as MySQL injection prevention, making HTTPS become REST API, using Json format for data ...). Howerver, this tutorial is dedicated for beginners to learn Arduino. We made it as simple as possible. After learning this tutorial, users can expand it.
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
※ OUR MESSAGES
-
You can share the link of this tutorial anywhere. Howerver, please do not copy the content to share on other websites. We took a lot of time and effort to create the content of this tutorial, please respect our work!
Follow Us
How To Create Database In Arduino
Source: https://arduinogetstarted.com/tutorials/arduino-mysql
Posted by: johnsonwhowerromed56.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Database In Arduino"
Post a Comment